[M] 542. 01 矩陣 (01 Matrix)
題目
- LeetCode 連結
- 主題:Graph, BFS, DP
- 難度:Medium
題目描述
給定一個 m x n 的二元矩陣 mat,請回傳一個同樣大小的矩陣,其中每個元素代表該位置與最近的 0 之間的距離。
相鄰的兩個單元格(共用一條邊)之間的距離為 1。
範例 1
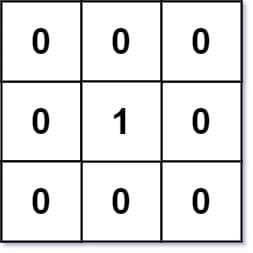
輸入:mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
輸出:[[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]範例 2
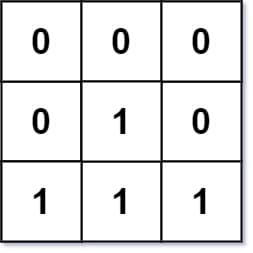
輸入:mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]]
輸出:[[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,2,1]]限制條件
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10⁴1 <= m * n <= 10⁴mat[i][j]只會是0或1mat至少包含一個0
相關題目
此題與 1765. Map of Highest Peak 相同。
問題釐清
- 題目的意思是如果該元素的值是 0,則與 0 的距離為 0,非 0 的話則要去找出與他相鄰最近的 0 的距離?
- 矩陣中一定會有一個 0?
- 矩陣的長寬至少爲 1?
提出測試案例
- 能通過兩個範例
- 能通過長寬為 1 的案例
- 能通過一個
5*5矩陣且只有一個 0 的案例 - 長寬皆為
10^4的壓測
提出思路
宣告一個塞滿 0 的二維陣列儲存結果,跑兩個迴圈去依序確認值是否為 0,不為 0 則去找前一個為 0 的座標計算距離。但這很明顯有機會不是最短距離。
因此後來看了 LeetCode 的官方教學後,提到最短距離的問題能直接聯想到 BFS,或還有另一種解法是用 DP,這裡先來學習一下 BFS 怎麼實作。
直覺地來解題的話我們可能會想要去找每個 1 的點離最近的 0 在哪裡,但這樣做演算法可能容易超時,假想一個 10000 * 10000 的矩陣只有某個角落為 0,則這樣的時間複雜度也就是操作次數會需要 10^8 次。
換個角度想如果我們以每個 0 為出發點,分別一層一層往外擴張去算周遭的座標的距離,那其實答案就很容易取得:
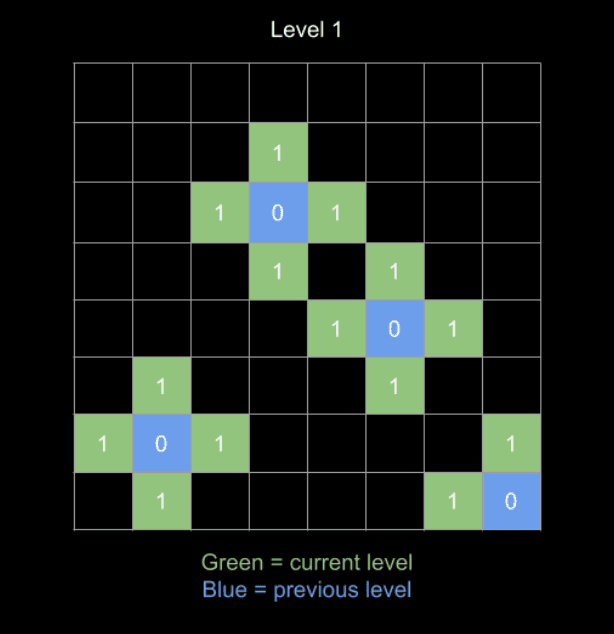
因此這個演算法會是這樣的思路,以註解表示:
function updateMatrix(mat: number[][]): number[][] {
// 宣告結果矩陣,使用 Infinity 為值順便確認沒有被造訪過
// 使用 queue 紀錄下一次要執行 BFS 擴展的座標
// 將所有值為 0 的座標放入 queue,並更新其結果陣列中的距離為 0
// 當 queue 不為空,跑 while 迴圈執行 BFS
// 對當前座標 4 個方向分別去紀錄其與 0 的距離
// 確保每個方向的座標在邊界內
// 且新座標還沒被訪問過,因此一開始初始化才要設 Infinity
// 把新座標加入 queue,進一步往外擴展並累加
// 回傳結果陣列
}實作
function updateMatrix(mat: number[][]): number[][] {
const width = mat.length;
const height = mat[0].length;
// 宣告結果矩陣,使用 Infinity 順便確認沒有被造訪過
const res = Array.from({ length: width }, () => Array(height).fill(Infinity));
// 使用 queue 紀錄所有為 0 的座標
const queue: [number, number][] = [];
// 將所有值為 0 的座標放入 queue,並更新其結果陣列中的距離為 0
for (let m = 0; m < width; m++) {
for (let n = 0; n < height; n++) {
if (mat[m][n] === 0) {
res[m][n] = 0;
queue.push([m, n]);
}
}
}
// 方向向量 (上, 下, 左, 右)
const directions = [
[-1, 0],
[1, 0],
[0, -1],
[0, 1],
];
// 執行 BFS
while (queue.length > 0) {
const [x, y] = queue.shift()!;
// 對當前座標每個方向去紀錄其與 0 的距離
for (const [dx, dy] of directions) {
const newX = x + dx;
const newY = y + dy;
// 確保每個方向的座標在邊界內
if (newX >= 0 && newX < width && newY >= 0 && newY < height) {
// 確認新座標還沒被訪問過,因此一開始才要設 Infinity
if (res[newX][newY] > res[x][y] + 1) {
res[newX][newY] = res[x][y] + 1;
// 把新座標加入 queue,進一步往外擴展並累加
queue.push([newX, newY]);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}撰寫測試
const testCases = [
{
mat: [
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
],
expected: [
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
],
},
{
mat: [
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
],
expected: [
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 2, 1],
],
},
{
mat: [[0]],
expected: [[0]],
},
{
mat: [
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
],
expected: [
[4, 3, 2, 3, 4],
[3, 2, 1, 2, 3],
[2, 1, 0, 1, 2],
[3, 2, 1, 2, 3],
[4, 3, 2, 3, 4],
],
},
];
describe('01 Matrix', () => {
test.each(testCases)(
'should return expected result for given matrix',
({ mat, expected }) => {
expect(updateMatrix(mat)).toEqual(expected);
}
);
// 壓測案例 (10^4 × 10^4 矩陣,只有左上角是 0)
test('should handle large matrix performance test', () => {
const largeTestSize = 10 ** 4;
const largeMat = Array.from({ length: largeTestSize }, () =>
Array(largeTestSize).fill(1)
);
largeMat[0][0] = 0;
const result = updateMatrix(largeMat);
expect(result[0][0]).toBe(0);
expect(result[largeTestSize - 1][largeTestSize - 1]).toBe(largeTestSize * 2 - 2);
});
});複雜度分析
- 時間複雜度:最多會跑過每個點一次,因此是
O(m * n) - 空間複雜度:使用的空間為宣告的 queue 與 res,因此是
O(m * n)
程式碼
詳細程式碼可以參考此 GitHub 連結。
