[H] 297. 序列化與反序列化二元樹 (Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree)
題目
- LeetCode 連結
- 主題:Binary Tree
- 難度:Hard
題目描述
序列化是將資料結構或物件轉換為位元序列的過程,以便將其儲存於檔案或記憶體緩衝區中,或透過網路連線進行傳輸,稍後在相同或其他環境中重組。
請設計一種演算法來序列化和反序列化二元樹。沒有任何限制此演算法如何運作,只要你的序列化/反序列化演算法確保能將二元樹序列化為字串,並且能從該字串正確地反序列化為原始的樹結構。
說明:輸入/輸出的格式可以與 LeetCode 的二元樹序列化格式相同。你不需要完全遵循該格式,可以發揮創意並提出不同的解法。
範例 1:
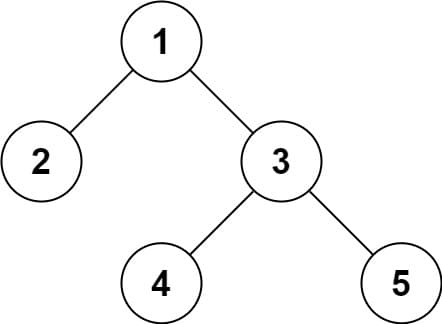
輸入:root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
輸出:[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]範例 2:
輸入:root = []
輸出:[]限制條件:
- 樹中結點的數量範圍為
[0, 10⁴]。 - 每個結點的值範圍為
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000。
問題釐清
- 簡單理解題意的話,會希望去完成兩個函式,讓一個二元樹在經過
serialize後成字串後,再把該字串傳入deserialize可以得到原本的二元樹,這樣理解沒錯吧? - 如果用 TypeScript 去實作的話,把這個可以做序列化、反序列化的功能做成一個像是 TreeCodec 的 class 可能會更好維護?
- 確認
serialize函式:- 輸入的型別部份限制為 TreeNode 或 null 即可,或需要處理其他不符合需求的格式做錯誤處理?
- 輸入的 TreeNode 中的值可以限制為 number,不需對其他非預期格式做處理?
- 當輸入中含有負值,則輸出可能會像是
-1,2,-3,n,n,-4,5這樣? - 輸出的部份一律為字串?
- 輸出的字串格式參考範例一的話,是否一定要像是
[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]的格式,或也可以簡化像是1,2,3,n,n,4,5即可? - 當輸入的樹在最後一層中只有一個最左邊的節點,則輸出字串中是否需移除連續的空值,像是
1,2,3,4,n,n,n其實只需要1,2,3,4即可 - 當輸入為 null 時,則輸出空字串?
- 確認
deserialize函式:- 輸入的型別部份限制為只有字串,會需要處理其他不符合需求的格式做錯誤處理?
- 輸出的部份為 TreeNode 或 null?
- 當輸入為空字串時,則輸出 null?
提出測試案例
- 基本測資能將範例一的
[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]做序列化、反序列化後能得到同樣的 tree - 確認空樹在序列化後得到空字串、將空字串反序列化後得到空樹 (null)
- 測試最後一層只有最左邊一個節點時,序列化後不會有連續的 n 字串
- 檢查含有負值的樹也能正確運作
- 檢查 root 節點值為 0 的狀況
- 檢查節點數為 10000 的只有右節點的樹能正確運作
- 檢查節點數接近 10000 的 complete binary tree 能正確運作
提出思路
定義好上述序列化與反序列化的規則後,可以視為逐層遍歷與字串處理問題:
- 定義
TreeCodec的 class,裡面包含serialize與deerialize兩個函式 - 序列化
- 若輸入為 null,回傳空字串
- 遍歷的演算法可以像做 Level Order Traversal 一樣用 BFS 來解
- 宣告一個 queue 來儲存每一層樹節點,跑迴圈來遍歷直到 queue 為空
- 依照類似
-1,2,-3,n,n,-4,5這樣的規則來輸出序列化字串資料,n 代表空節點,且可能有負數值 - 移除多餘的連續空值
- 組合字串陣列並以
,做分隔 - 返回結果字串
- 反序列化
- 若輸入為空字串,回傳 null
- 對輸入字串用
,符號做 split 得到節點值的陣列 - 對該字串陣列值做處理,遇到
n則視為空節點 null,否則轉為數字 - 用 queue 儲存當前待處理的節點,並跑迴圈用 top down 的方式來逐層組合輸出的二元樹,直到 queue 為空則停止
- 返回結果二元樹
以註解表示:
// declare a TreeCodec class including following two functions
/*
* Encodes a tree to a single string.
*/
function serialize(root: TreeNode | null): string {
// if root is null, return empty string
// declare a result string array
// declare a queue to do level order traversal, init with root value
// run a while loop when queue is not empty
// dequeue to get current node
// if current node not null
// push value into result
// enqueue left node and right node
// push null value
// remove redundant null value at tail
// return serialized string by joining with `,`
}
/*
* Decodes your encoded data to tree.
*/
function deserialize(data: string): TreeNode | null {
// if data is empty string, return null
// split string by `,`
// transform each value to null or number
// declare result tree
// declare a queue, init with first node
// run a while loop when queue is not empty
// dequeue current node
// assign next value as left node if it's not null
// assign next value as right node if it's not null
// return result tree
}實作
將上述的思路實作後會像以下的程式:
// declare a TreeCodec class including following two functions
class TreeCodec {
/*
* Encodes a tree to a single string.
*/
serialize(root: TreeNode | null): string {
// if root is null, return empty string
if (root === null) {
return '';
}
// declare a result string array
const result: string[] = [];
// declare a queue to do level order traversal, init with root value
const queue: (TreeNode | null)[] = [root];
// run a while loop when queue is not empty
while (queue.length > 0) {
// dequeue to get current node
const currentNode = queue.shift();
// if current node not null
if (currentNode) {
// push value into result
result.push(currentNode.val.toString());
// enqueue left node and right node
queue.push(currentNode.left);
queue.push(currentNode.right);
} else {
result.push('n');
}
}
// remove redundant null value at tail
while (result[result.length - 1] === 'n') {
result.pop();
}
// return serialized string by joining with `,`
return result.join(',');
}
/*
* Decodes your encoded data to tree.
*/
deserialize(data: string): TreeNode | null {
// if data is empty string, return null
if (data === '') {
return null;
}
// split string by `,`
// transform each value to null or number
const values = data.split(',').map((v) => (v === 'n' ? null : Number(v)));
// preventing wrong data format with empty root value
if (typeof values[0] !== 'number') {
throw new Error('wrong input data');
}
// declare result tree
const root = new TreeNode(values[0]);
// declare a queue, init with first node
const queue = [root];
let currentIndex = 1;
// run a while loop when queue is not empty
while (queue.length > 0) {
// dequeue current node
const node = queue.shift() as TreeNode;
// assign next value as left node if it's not null
if (typeof values[currentIndex] === 'number') {
node.left = new TreeNode(values[currentIndex]!);
queue.push(node.left);
}
currentIndex++;
// assign next value as right node if it's not null
if (typeof values[currentIndex] === 'number') {
node.right = new TreeNode(values[currentIndex]!);
queue.push(node.right);
}
currentIndex++;
}
// return result tree
return root;
}
}試著將這段程式中的兩個函式放到 leetcode 上去 submit 可以通過,以下試著來根據上面的測試案例實作單元測試。
撰寫單元測試
describe('Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree', () => {
const codec = new TreeCodec();
it('should correctly serialize and deserialize for example 1', () => {
const root = new TreeNode(
1,
new TreeNode(2),
new TreeNode(3, new TreeNode(4), new TreeNode(5))
);
const serialized = codec.serialize(root);
const deserialized = codec.deserialize(serialized);
expect(serialized).toEqual('1,2,3,n,n,4,5');
expect(deserialized).toEqual(root);
});
it('should handle empty tree for example 2', () => {
const root = null;
const serialized = codec.serialize(root);
const deserialized = codec.deserialize(serialized);
expect(serialized).toEqual('');
expect(deserialized).toBeNull();
});
it('should handle tree with only leftmost node in the last level', () => {
const root = new TreeNode(
1,
new TreeNode(2, new TreeNode(4)),
new TreeNode(3)
);
const serialized = codec.serialize(root);
expect(serialized).toEqual('1,2,3,4');
});
it('should handle tree with negative values', () => {
const root = new TreeNode(
-1,
new TreeNode(-2),
new TreeNode(-3, new TreeNode(-4), new TreeNode(-5))
);
const serialized = codec.serialize(root);
const deserialized = codec.deserialize(serialized);
expect(serialized).toEqual('-1,-2,-3,n,n,-4,-5');
expect(deserialized).toEqual(root);
});
it('should handle tree with root value of 0', () => {
const root = new TreeNode(0, new TreeNode(-1), new TreeNode(1));
const serialized = codec.serialize(root);
const deserialized = codec.deserialize(serialized);
expect(serialized).toEqual('0,-1,1');
expect(deserialized).toEqual(root);
});
it('should handle tree with 10000 nodes having only left children', () => {
const root = new TreeNode(1);
let current = root;
for (let i = 2; i <= 10000; i++) {
const newNode = new TreeNode(i);
current.left = newNode;
current = newNode;
}
const serialized = codec.serialize(root);
const deserialized = codec.deserialize(serialized);
expect(serialized.startsWith('1,2,n,3,n,4,n')).toBeTruthy();
expect(deserialized).toEqual(root);
});
it('should handle a complete binary tree with lots of nodes', () => {
const createCompleteBinaryTree = (n: number): TreeNode | null => {
if (n === 0) return null;
const nodes = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => new TreeNode(i + 1));
for (let i = 0; i < Math.floor(n / 2); i++) {
if (2 * i + 1 < n) nodes[i].left = nodes[2 * i + 1];
if (2 * i + 2 < n) nodes[i].right = nodes[2 * i + 2];
}
return nodes[0];
};
const root = createCompleteBinaryTree(10000);
const serialized = codec.serialize(root);
const deserialized = codec.deserialize(serialized);
expect(deserialized).toEqual(root);
});
});這裡實際去執行測試後,只有倒數第二個這個左側一條深層的樹會遇到 RangeError: Maximum call stack size exceeded 的 stack overflow 問題而失敗。
先試著把反序列化的部份註解掉就能正常通過了,所以效能瓶頸是發生在 deserialized 的地方,試著做一些特製的邊界條件去調整後問題還是存在,後來在想有可能是原本 Vitest 設定可能有一些效能相關的問題。
找到一個 pool 的設定,試著調整成 pool: ‘threads' 就通過了,研究了下文件看起來預設是使用 pool: 'forks' 的方式,也就是將每個測試跑在不同的 node:child_process,而若有效能問題,文件建議可以改成用 node:worker_threads 的方式改善。
又好奇去看這是不是只有 Vitest 特製的設定,找到 jest 中也有一個 workerThreads 的設定,關於這兩者的差別還沒太深入研究,先筆記在這。
程式碼
完整程式碼可以參考此 GitHub 連結。
