[E] 206. 反轉鏈結串列 (Reverse Linked List)
題目
- LeetCode 連結
- 主題:Linked List
- 難度:Easy
題目描述
給定一個單向鏈結串列的頭節點 head,請反轉該鏈結串列,並回傳反轉後的串列。
範例 1:
輸入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
輸出:[5,4,3,2,1]範例 2:
輸入:head = [1,2]
輸出:[2,1]範例 3:
輸入:head = []
輸出:[]限制條件:
- 鏈結串列的節點數量範圍為
[0, 5000]。 -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
進階挑戰:
鏈結串列可以透過迭代或遞迴的方式進行反轉。你能實作這兩種方式嗎?
問題釐清
- 輸入型別一定是 ListNode 或空串列的 null 嗎,應該不需要處理不合法輸入?
- 當輸入為 null 時則回傳 null?
- 節點的數量限制在 5000 個內?會需要考慮 stack overflow 的問題嗎?
提出測試案例
- 能通過三個範例
- 節點數量的壓測
提出思路
如果以程式的簡潔程度來實作的話,使用遞迴應該是最快,但如果需要考量較大量的節點數量可能需要改成迭代的方式。這裡先以遞迴方式實作,如果是遞迴的話,關鍵在於找出 base case 與要執行遞迴的剩餘部份。
如果以一個最簡單的例子 1 → 2 → 3 這樣的串列來做圖解的話,步驟會像是這樣:
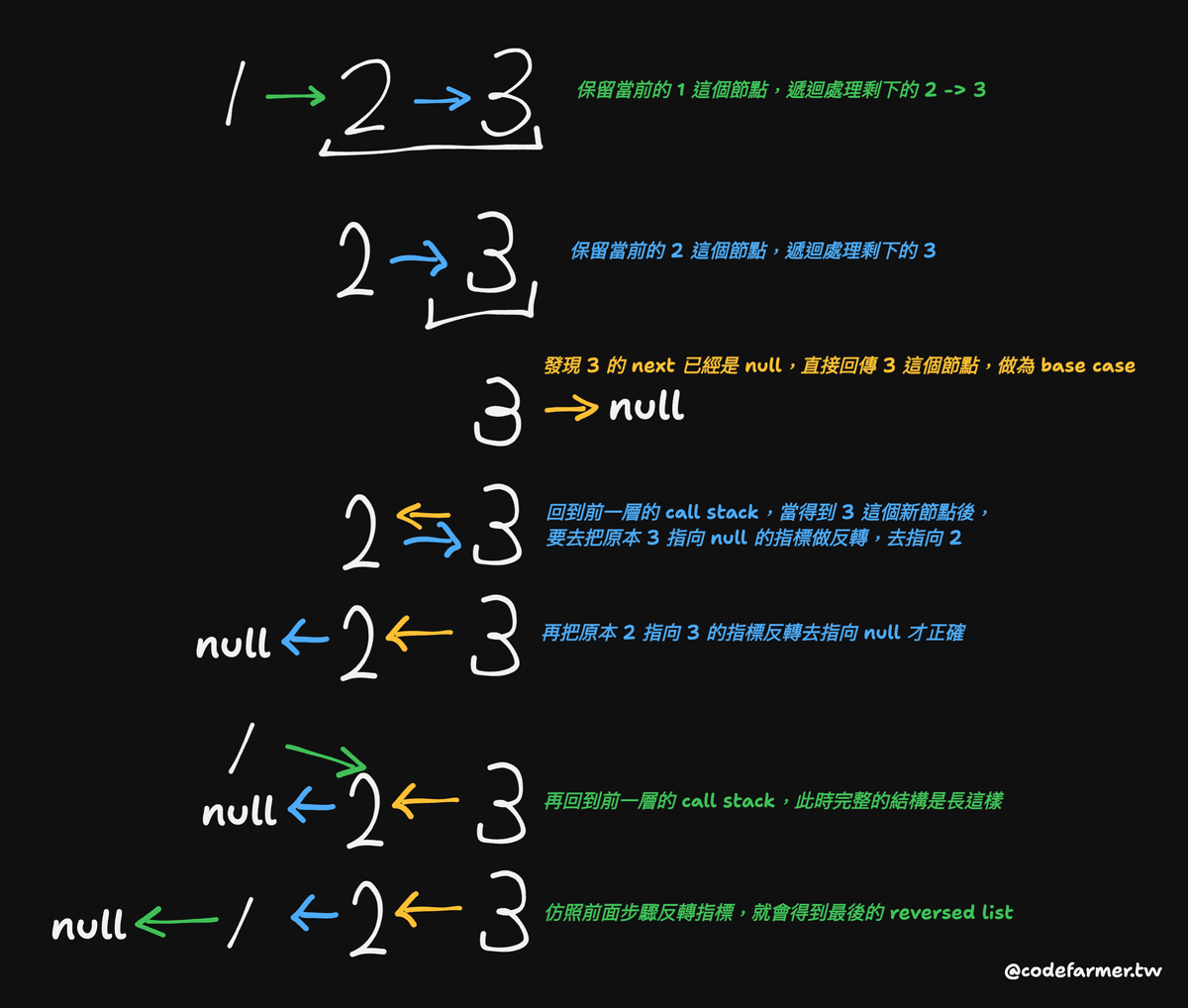
因此實作上的思路大概會像這樣:
- 處理 base cases:當
head或head.next為null時,代表已經到了尾部,則直接回傳head這個節點 - 宣告一個新的串列去遞迴處理該節點後的剩餘串列節點
- 反轉當前
head節點的head.next.next與head.next指標 - 回傳處理後的新串列的頭部
以註解表示思路的話會像這樣:
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
// recursive function base cases, if head or head.next is null, return head
// declare a new list to reverse remaining list nodes recursively
// reverse the pointer for current node
// return new list
}實作
function reverseList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
// recursive function base cases, if head or head.next is null, return head
if (head === null || head.next === null) {
return head;
}
// declare a new list to reverse remaining list nodes recursively
const newList = reverseList(head.next);
// reverse the pointer for current node
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
// return new list
return newList;
}撰寫測試
沿用之前實作的陣列、串列互轉的 util function,可以簡單用 test.each 寫個單元測試像這樣:
describe('Reverse Linked List', () => {
test.each([
{ input: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], expected: [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] },
{ input: [1, 2], expected: [2, 1] },
{ input: [], expected: [] },
])('should correctly reverse the list %j', ({ input, expected }) => {
const head = createLinkedList(input);
const reversedHead = reverseList(head);
const result = linkedListToArray(reversedHead);
expect(result).toEqual(expected);
});
test('Stress Test: Reversing a list with 5000 nodes', () => {
const inputArray = Array.from({ length: 5000 }, (_, i) => i + 1);
const head = createLinkedList(inputArray);
const reversedHead = reverseList(head);
const result = linkedListToArray(reversedHead);
const expectedArray = inputArray.reverse();
expect(result).toEqual(expectedArray);
});
});在壓測這裡如果嘗試去增加節點數會發現遇到 Maximum call stack size exceeded 的問題,下面再來嘗試用進階挑戰中提到的迭代方式改寫看看。
實作迭代解法
詳細的思路用圖解比較好理解,簡單說就是用兩個指標來依序跑迴圈去不斷重複執行「斷開連結與反轉」直到當前指標指到 null 為止:
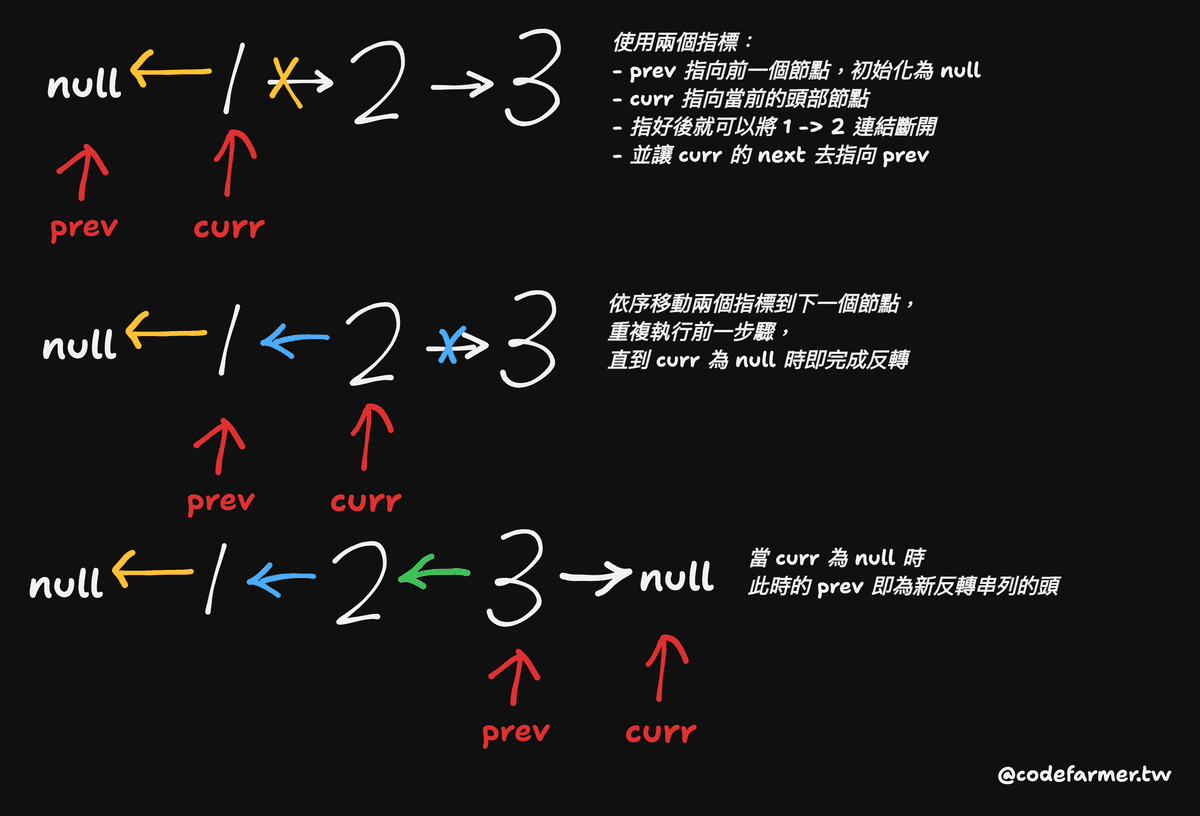
實作的話就會像這樣:
function reverseListIteratively(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
// if head is null, return null
if (head === null) {
return null;
}
// declare two pointer to record prev node and curr node
let prev: ListNode | null = null;
let curr: ListNode | null = head;
// run a while loop until curr === null
while (curr !== null) {
const tmpNext: ListNode | null = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = tmpNext;
}
// return prev node as head of new list
return prev;
}複雜度分析
| 遞迴 | 迭代 | |
|---|---|---|
| 時間複雜度 | O(N) | O(N) |
| 空間複雜度 | O(N) | O(1) |
| 說明 | 遞迴會佔用額外的 Call Stack,最多會遞迴到 N 層 (節點數量)。 | 只使用了固定數量的變數 (prev、curr、tmpNext),不會隨著輸入大小增加 |
程式碼
詳細程式碼可以參考此 GitHub 連結。
