[E] 141. 鏈結串列中的環 (Linked List Cycle)
題目
- LeetCode 連結
- 主題:Linked List, Two Pointers
- 難度:Easy
題目描述
給定一個鏈結串列的頭節點 head,判斷該鏈結串列是否包含環。
如果在鏈結串列中有某個節點可以通過不斷跟隨 next 指標再次到達該節點,則說明該鏈結串列中存在環。在內部,變數 pos 表示尾節點的 next 指向的節點索引位置(0 起始)。注意,pos 不是作為參數傳入的。
如果鏈結串列中存在環,返回 true;否則,返回 false。
範例 1
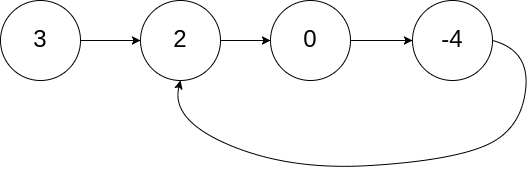
輸入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
輸出:true
解釋:鏈結串列中存在一個環,其中尾節點連接到第 1 個節點(索引從 0 開始)。
範例 2
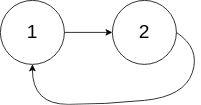
輸入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
輸出:true
解釋:鏈結串列中存在一個環,其中尾節點連接到第 0 個節點。
範例 3
輸入:head = [1], pos = -1
輸出:false
解釋:鏈結串列中沒有環。
限制條件
- 鏈結串列的節點數量範圍為
[0, 10^4]。 -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5pos為-1或是鏈結串列中有效的索引。
進階挑戰
你能在 O(1) 記憶體(即常數空間)內解決此問題嗎?
問題釐清
- 題目中範例的
pos看起來是測試時用來標記環的位置,不會在函式中去傳入,所以只能以當前的 linked list 來判斷是否有環,這樣理解沒錯? - 如果輸入是空串列,應為 false?
提出測試案例
會需要處理 array to linked list 的轉換,並使用 pos 這個參數來製作環做為輸入測試資料,可能會有以下幾個案例:
- 題目的三個範例
- 空串列,應為 false
- 超過
10^4的節點數量壓測
提出思路
直覺想到可以直接用一個 map 與 while 迴圈來解,從 head 開始一層一層往下找,並紀錄造訪過的節點值到 map 中,並確認其 next 是否有出現過,有的話則代表有環,回傳 true,當下個節點為 null 時則迴圈中斷,回傳 false。
以註解表示以上的思路:
function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
// edge case: head = null, return false
// declare a value map for check cycle
// run a while loop to check whether next is null or not
// record value into map
// check current.next hit the map or not
// return false
}實作
一開始實作了這樣的版本:
function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
// edge case: head = null, return false
if (head === null) {
return false;
}
// declare a value map for check cycle
const seen = new Set<number>();
let current = head;
// run a while loop to check whether next is null or not
while (current.next !== null) {
// check current.next hit the map or not
if (seen.has(current.next.val)) {
return true;
} else {
// record value into map
seen.add(current.val);
current = current.next;
}
}
return false;
}但拿去 LeetCode 上 submit 時遇到某個測資錯誤:
輸入:head = [-21,10,17,8,4,26,5,35,33,-7,-16,27,-12,6,29,-12,5,9,20,14,14,2,13,-24,21,23,-21,5], pos = -1
輸出:false後來想到是犯傻了不應該是只有記值到 Set 中而是要記整個 ListNode 才對,稍微修正一下:
function hasCycle(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
// edge case: head = null, return false
if (head === null) {
return false;
}
// declare a value map for check cycle
const seen = new Set<ListNode>();
let current = head;
// run a while loop to check whether next is null or not
while (current.next !== null) {
// check current.next hit the map or not
if (seen.has(current.next)) {
return true;
} else {
// record value into map
seen.add(current);
current = current.next;
}
}
return false;
}撰寫測試
這裡會需要用 pos 另外寫一個 helper function,可以去做出一個有環的 linked list,完整程式碼參考這裡:
const createLinkedListWithCycle = (values: number[], pos: number) => {
const head = createLinkedList(values);
if (pos === -1 || !head) return head;
let tail = head;
let cycleNode = null;
let index = 0;
while (tail.next !== null) {
if (index === pos) {
cycleNode = tail;
}
tail = tail.next;
index++;
}
if (cycleNode) tail.next = cycleNode;
return head;
};接著就能用以上的 helper function 搭配上面的測試案例做出這樣的測試:
describe('Linked List Cycle', () => {
it.each([
{
input: { values: [3, 2, 0, -4], pos: 1 },
expected: true
},
{
input: { values: [1, 2], pos: 0 },
expected: true
},
{
input: { values: [1], pos: -1 },
expected: false
},
{
input: { values: [], pos: -1 },
expected: false
},
{
input: {
values: [
-21, 10, 17, 8, 4, 26, 5, 35, 33, -7, -16, 27, -12, 6, 29, -12, 5, 9,
20, 14, 14, 2, 13, -24, 21, 23, -21, 5
],
pos: -1
},
expected: false
}
])('should detect cycle for input $input', ({ input, expected }) => {
const head = createLinkedListWithCycle(input.values, input.pos);
expect(hasCycle(head)).toBe(expected);
});
it('Stress Test: should handle a list with less than 10^4 nodes with a cycle', () => {
const inputArray = Array.from({ length: 10 ** 4 }, (_, i) => i + 1);
const head = createLinkedListWithCycle(inputArray, 0);
expect(hasCycle(head)).toBe(true);
});
});複雜度分析
- 時間複雜度:一個迴圈,且最壞狀況是碰到長度為 n 的串列,一路檢查到最後,也就會是
O(n) - 空間複雜度:這裡用一個 Set 去紀錄曾經造訪過的節點,最差情況下會是
O(n)
進階挑戰或其他解法探索
如果要將上面的空間複雜度壓在 O(1) 內,從 LeetCode 教學上看起來還可以用快慢指標的 two pointers 方式來解。
關於快慢指標覺得裡面的教材比喻蠻生動的:「想像一下兩個跑步者在跑道上以不同的速度奔跑。當軌道實際上是一個圓圈時會發生什麼?」
也就是說當今天有 slow 與 fast 兩個指標一個一次走一步、一個一次走兩步,當 fast 能順利走完到最後 null,則代表跑道中沒有環;反之當今天 fast 開始比 slow 落後時,則代表串列中有環。
function hasCycleWithTwoPointers(head: ListNode | null): boolean {
if (head === null) {
return false;
}
let slow: ListNode | null = head;
let fast: ListNode | null = head.next;
while (slow !== fast) {
if (fast === null || fast.next === null) {
return false;
}
slow = slow?.next ?? null;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}換成這個演算法實測後,比較一下用 TypeScript 的效能提升多少:
- 時間:
79ms (24.18%)→59ms (97.02%) - 空間:
55.2M (21.45%)→53.91M (74.69%)
冷知識:這個解法又被稱為 Floyd's Cycle Detection Algorithm(佛洛伊德環檢測演算法)
程式碼
詳細程式碼可以參考此 GitHub 連結。
